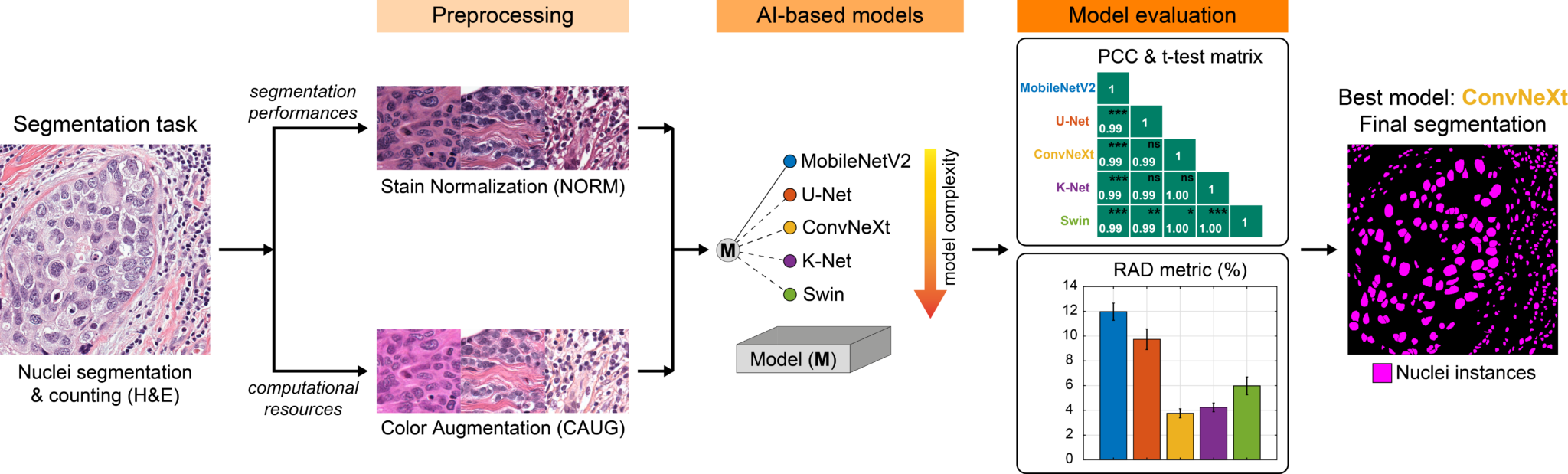
Shifting the Focus of Digital Pathology: The Raising Relevance of Pre-Processing Phase Over Model Complexity
IET Image Processing | 27/01/2026Recent trends in computational pathology favour increasingly complex deep learning architectures, raising the question of whether such complexity is necessary for routine diagnostic tasks. This study challenges this assumption through a comprehensive analysis of the relationship between model complexity, data pre-processing, and performance across four fundamental digital pathology tasks.
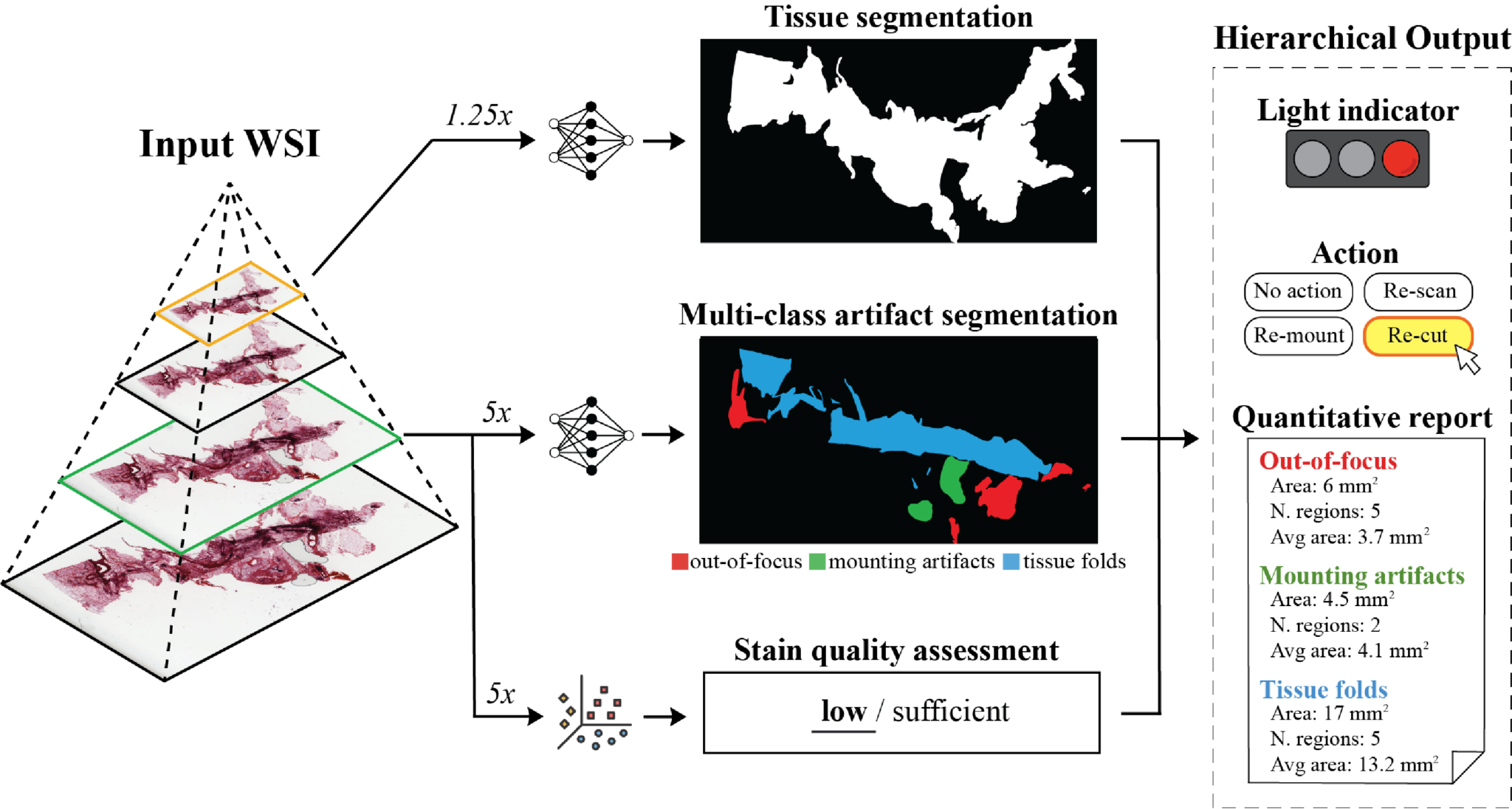
SlideInspect: From Pixel-Level Artifact Detection to Actionable Quality Metrics in Digital Pathology
International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology | 11/01/2026The presence of artifacts in whole slide images (WSIs), such as tissue folds, air bubbles, and out- of-focus regions, can significantly impact WSI digitization, pathologists’ evaluation, and the accuracy of downstream analyses. We present SlideInspect, a novel AI-based framework for comprehensive artifact detection and quality control in digital pathology.
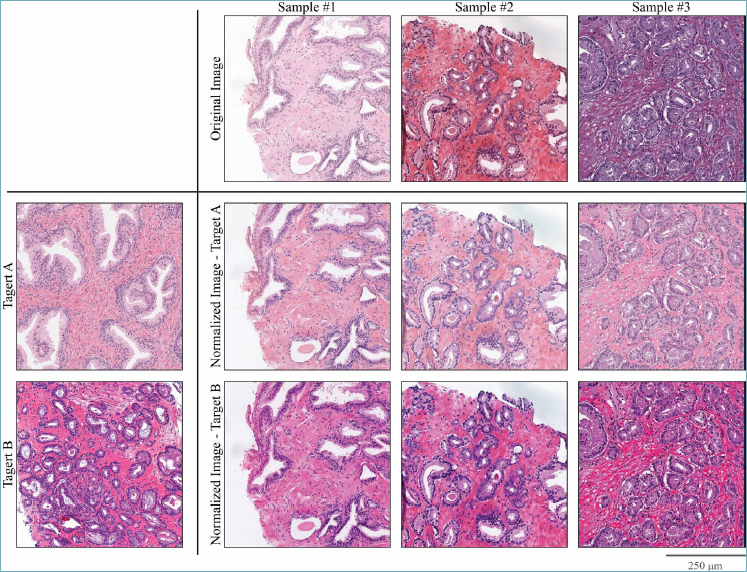
Not all stains are made equal: impact of stain normalization on prostate cancer diagnosis
PATHOLOGICA | 29/11/2024Stain normalization is a technique used to standardize the color appearance of digital whole slide images (WSIs). This study aimed to assess the impact of digital stain normalization on prostate cancer diagnosis by pathologists.
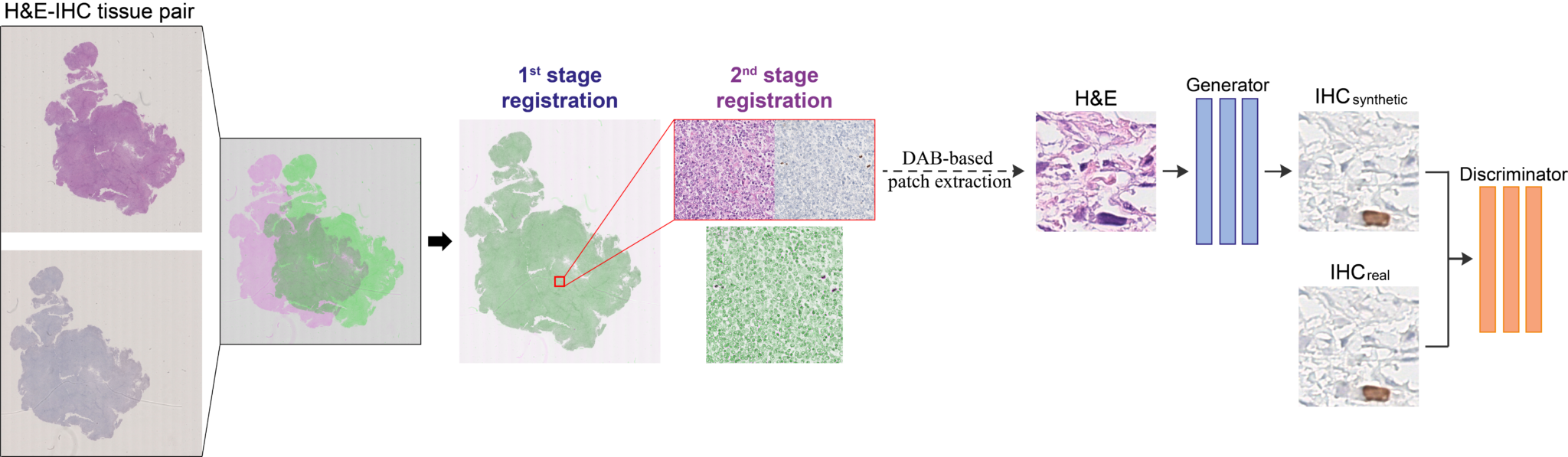
Computational Synthesis of Histological Stains: A Step Toward Virtual Enhanced Digital Pathology
International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology | 04/09/2024Traditional methods like hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) primarily offer morphological information but lack insight into functional details, such as the expression of biomarkers indicative of cellular activity. To overcome this limitation, we propose a computational approach to synthesize virtual immunohistochemical (IHC) stains from H&E input, transferring imaging features across staining domains.
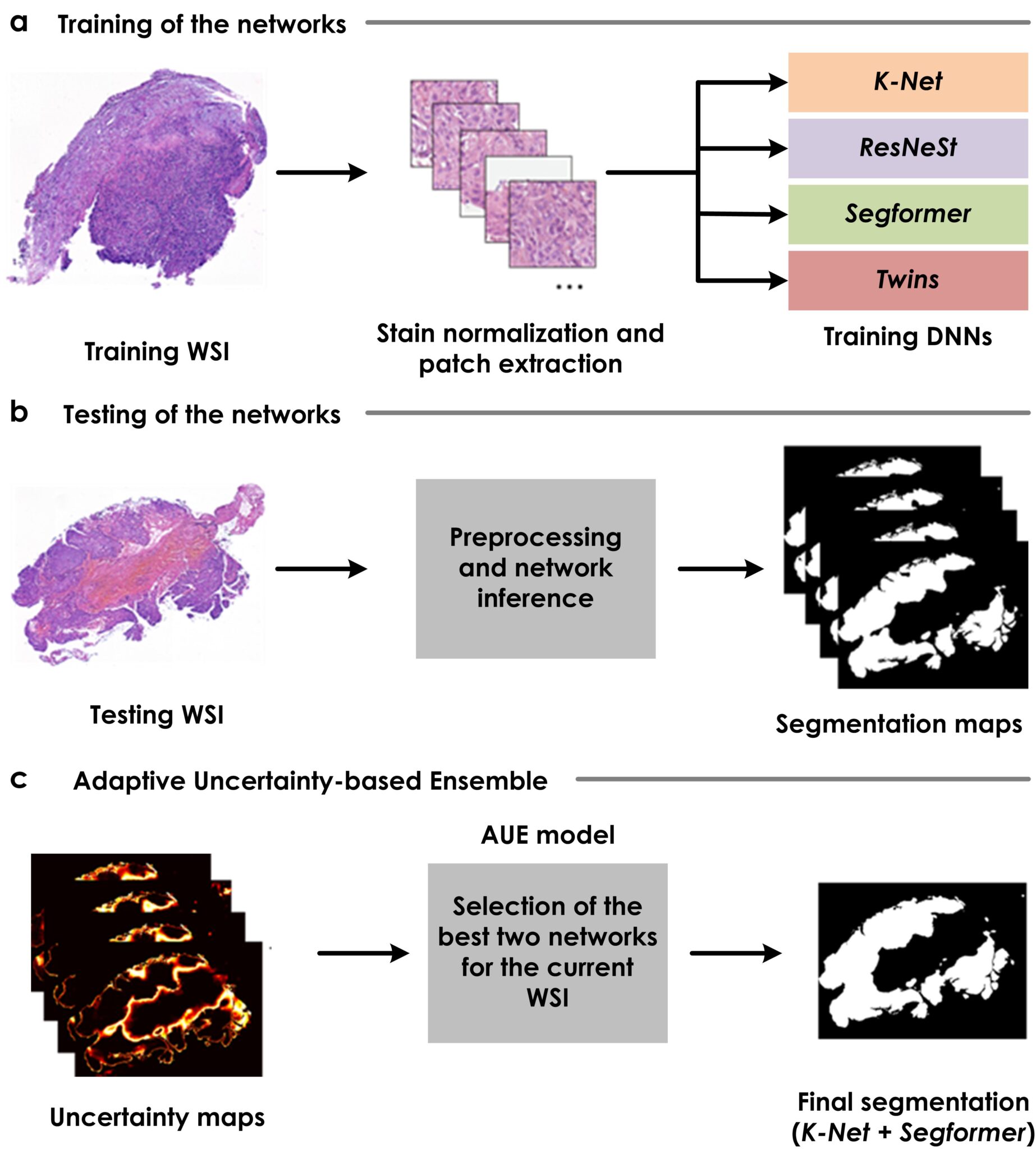
A dynamic uncertainty-aware ensemble model: Application to lung cancer segmentation in digital pathology
Applied Soft Computing | 05/08/2024Ensemble models have emerged as a powerful technique for improving robustness in medical image segmentation. However, traditional ensembles suffer from limitations such as under-confidence and over-reliance on poor performing models. In this work, we introduce an Adaptive Uncertainty-based Ensemble (AUE) model for tumor segmentation in histopathological slides.
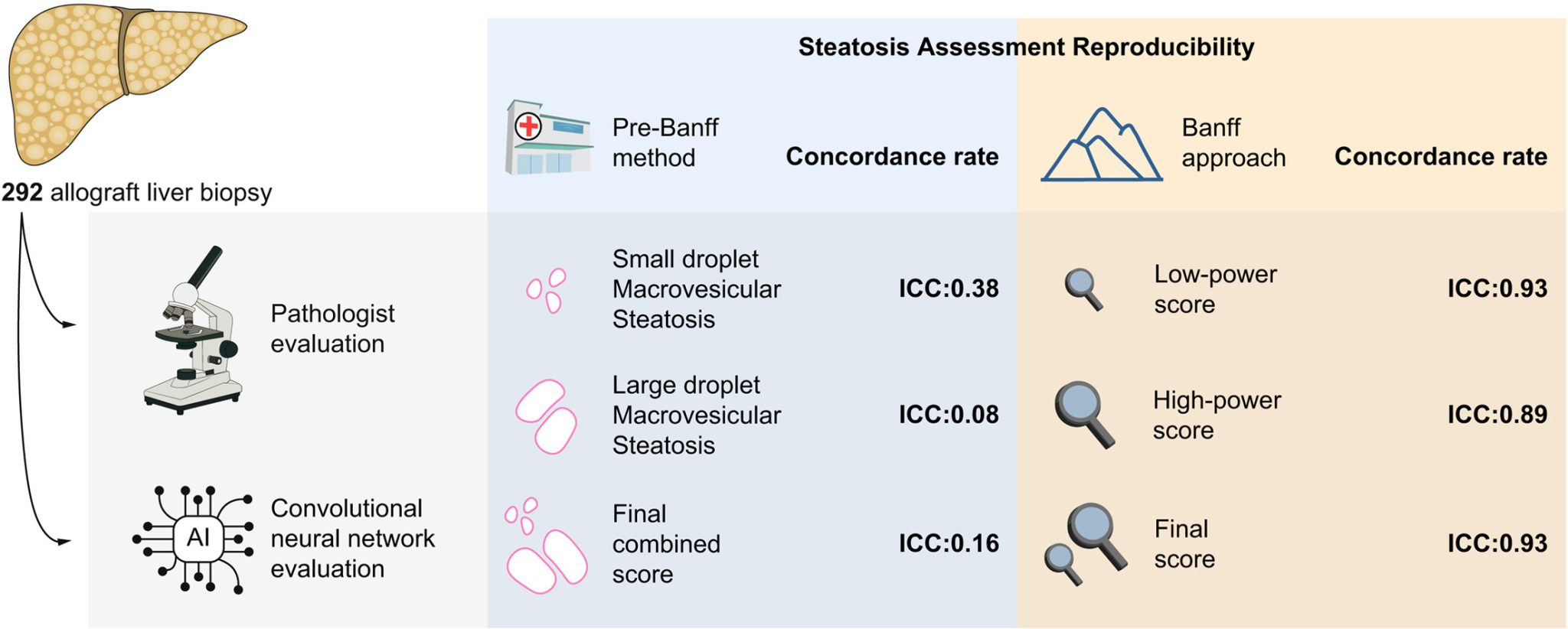
Improved assessment of donor liver steatosis using Banff consensus recommendations and deep learning algorithms
Journal of Hepatology | 28/11/2023The Banff Liver Working Group recently published consensus recommendations for steatosis assessment in donor liver biopsy, but few studies reported their use and no automated deep-learning algorithms based on the proposed criteria have been developed so far.
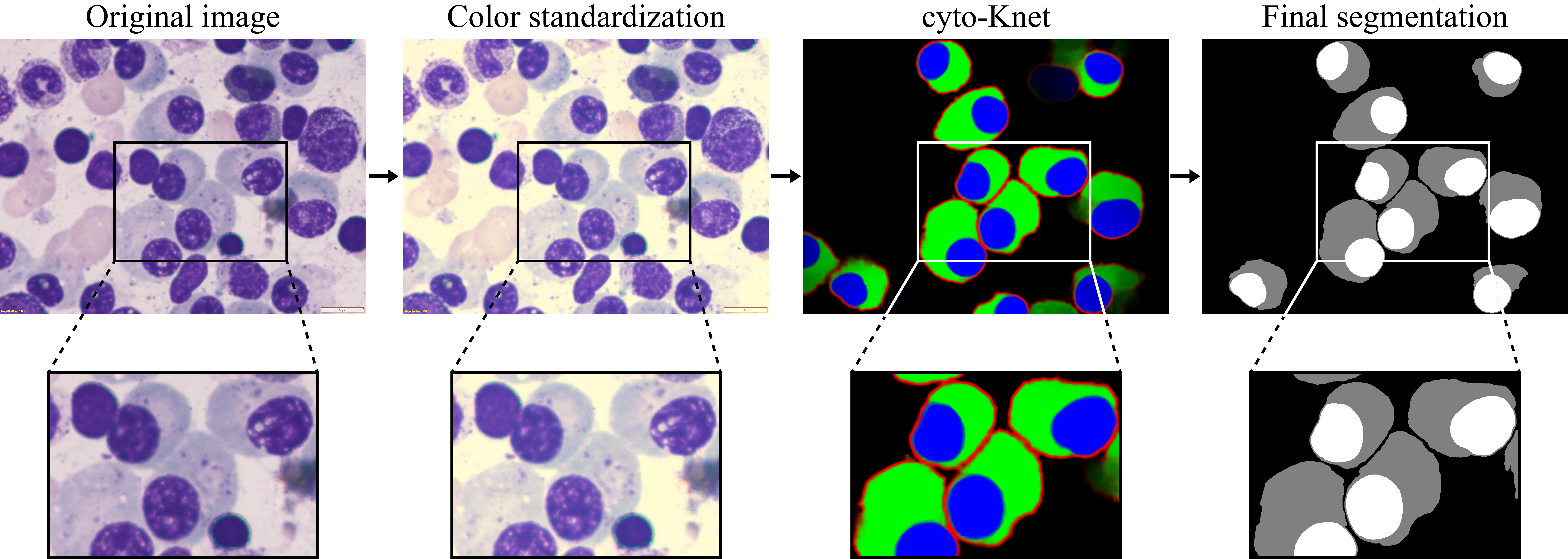
cyto-Knet: An instance segmentation approach for multiple myeloma plasma cells using conditional kernels
International Journal of Imaging Systems and Technology | 25/10/2023Multiple myeloma disrupts normal blood cell production, requiring early detection due to the increased risk of bone metastases. Although various artificial intelligence (AI) methods have been developed to assist pathologists, they often lack comprehensive metrics to measure both detection and segmentation errors.
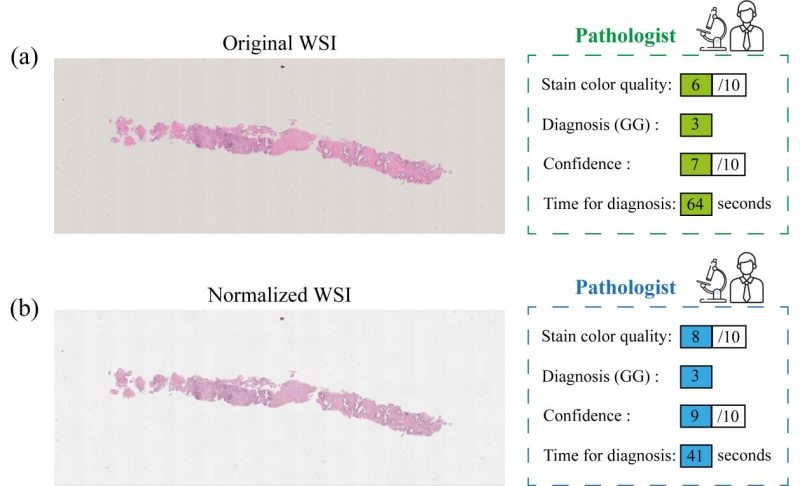
Impact of Stain Normalization on Pathologist Assessment of Prostate Cancer: A Comparative Study
Cancers | 27/02/2023Prostate cancer is the second most diagnosed cancer in men worldwide, with an estimated 1,276,000 new cases and 359,000 deaths in 2018. It is graded using the Gleason system into five grade groups of increasing tumor aggressiveness. However, diagnosis is hampered by a relatively high rate of inter- and intra-observer variability. Currently, the reduction of the perceived color variability is performed by physical quality controls, such as subjective assessment by visual inspection and comparison between laboratories.
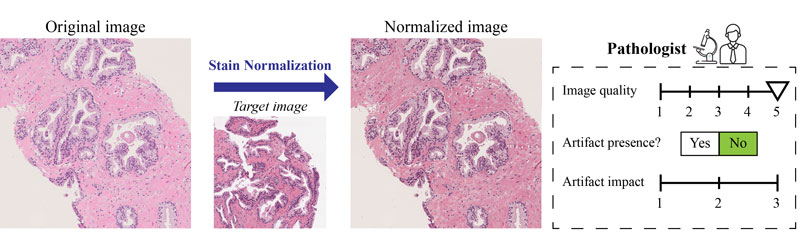
Stain normalization in digital pathology: Clinical multi-center evaluation of image quality
Journal of Pathology Informatics | 24/09/2022In digital pathology, the final appearance of digitized images is affected by several factors, resulting in stain color and intensity variation. Stain normalization is an innovative solution to overcome stain variability.
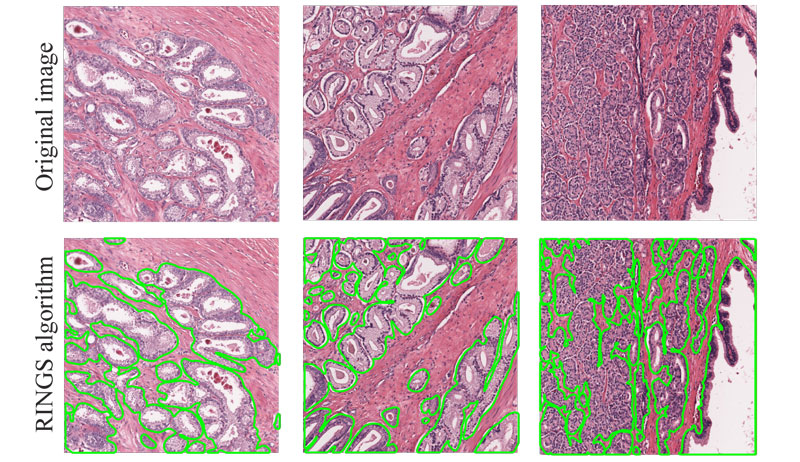
A hybrid deep learning approach for gland segmentation in prostate histopathological images
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine | 16/04/2021In digital pathology, the morphology and architecture of prostate glands have been routinely adopted by pathologists to evaluate the presence of cancer tissue. The manual annotations are operator-dependent, error-prone and time-consuming. The automated segmentation of prostate glands can be very challenging too due to large appearance variation and serious degeneration of these histological structures.
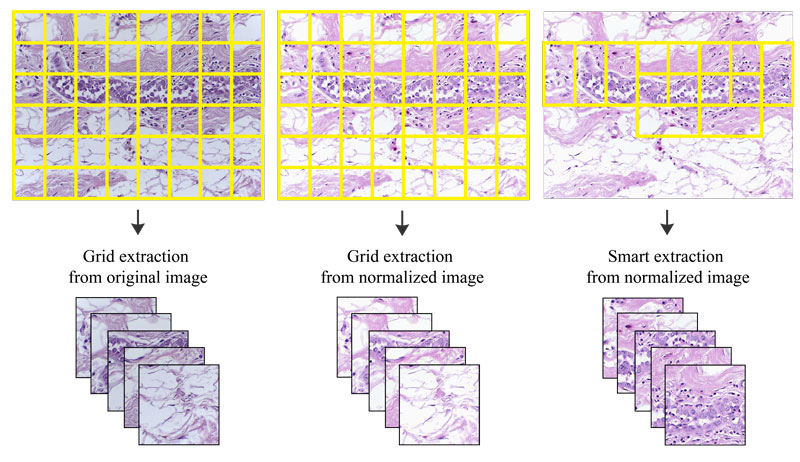
Impact of stain normalization and patch selection on the performance of convolutional neural networks in histological breast and prostate cancer classification
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update | 13/02/2021Recently, deep learning has rapidly become the methodology of choice in digital pathology image analysis. However, due to the current challenges of digital pathology (color stain variability, large images, etc.), specific pre-processing steps are required to train a reliable deep learning model.
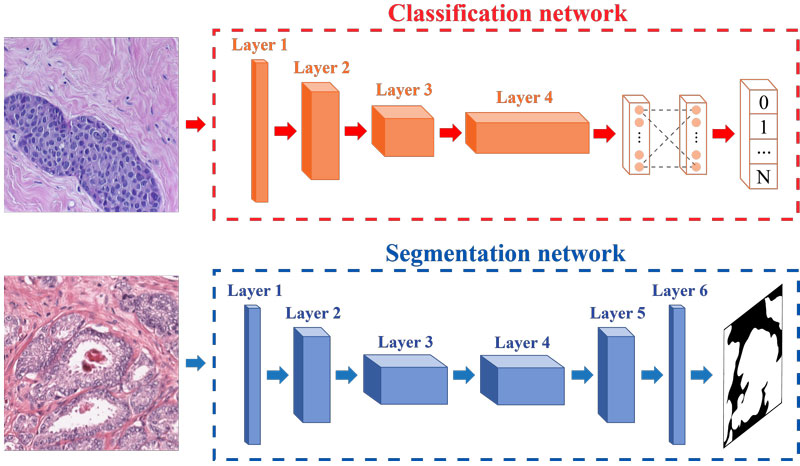
The impact of pre- and post-image processing techniques on deep learning frameworks: A comprehensive review for digital pathology image analysis
Computers in Biology and Medicine | 21/11/2020Recently, deep learning frameworks have rapidly become the main methodology for analyzing medical images. Due to their powerful learning ability and advantages in dealing with complex patterns, deep learning algorithms are ideal for image analysis challenges, particularly in the field of digital pathology.
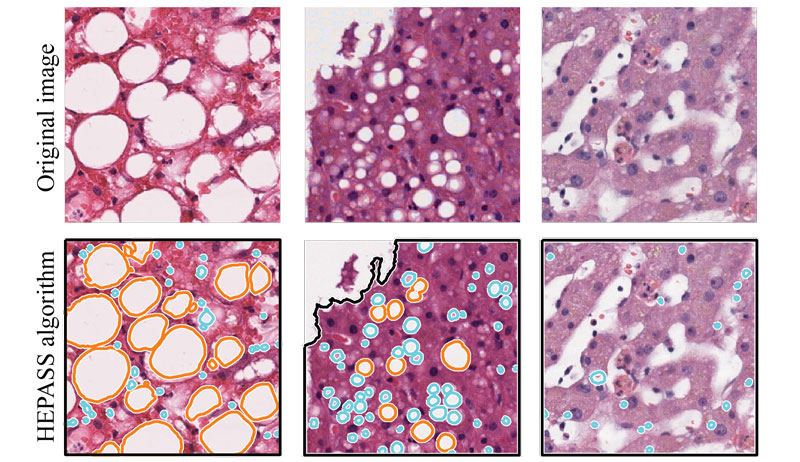
Fully automated quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis in liver transplants
Computers in Biology and Medicine | 29/05/2020The presence of macro- and microvesicular steatosis is one of the major risk factors for liver transplantation. An accurate assessment of the steatosis percentage is crucial for determining liver graft transplantability, which is currently based on the pathologists’ visual evaluations on liver histology specimens.
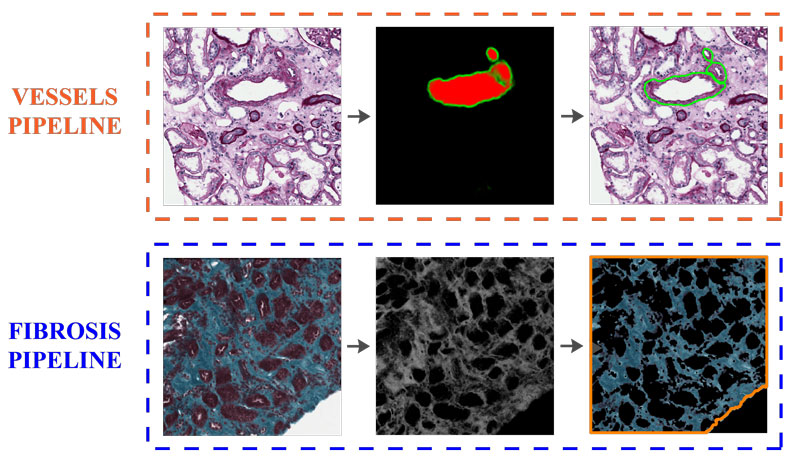
Karpinski Score under Digital Investigation: A Fully Automated Segmentation Algorithm to Identify Vascular and Stromal Injury of Donors’ Kidneys
Electronics | 08/10/2020In kidney transplantations, the evaluation of the vascular structures and stromal areas is crucial for determining kidney acceptance, which is currently based on the pathologist’s visual evaluation. In this context, an accurate assessment of the vascular and stromal injury is fundamental to assessing the nephron status.
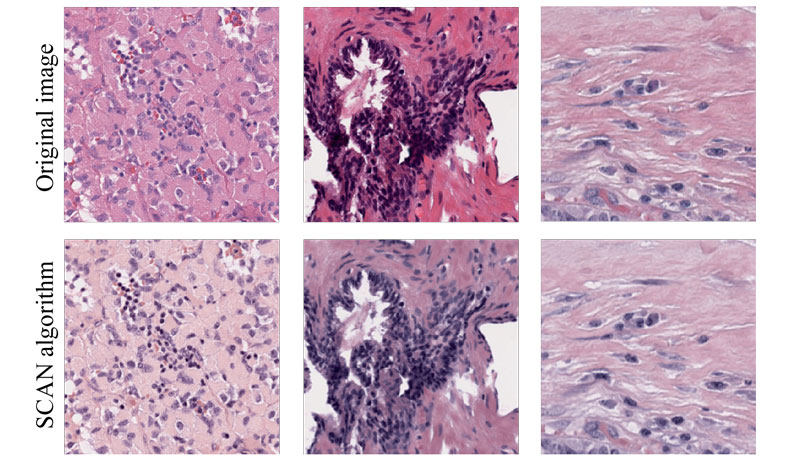
Stain Color Adaptive Normalization (SCAN) algorithm: Separation and standardization of histological stains in digital pathology
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine | 17/04/2020The diagnosis of histopathological images is based on the visual analysis of tissue slices under a light microscope. However, the histological tissue appearance may assume different color intensities depending on the staining process, operator ability and scanner specifications. This stain variability affects the diagnosis of the pathologist and decreases the accuracy of computer-aided diagnosis systems.
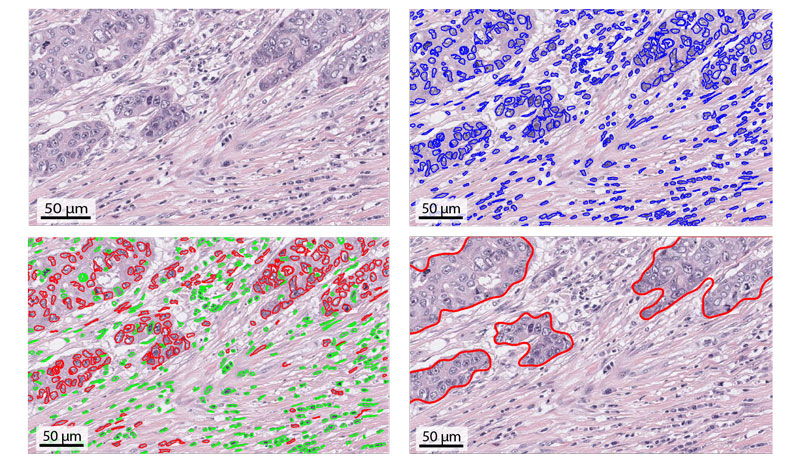
Automatic discrimination of neoplastic epithelium and stromal response in breast carcinoma
Computers in Biology and Medicine | 11/05/2019In breast carcinoma, epithelial–stromal interactions play a pivotal role in tumor formation and progression, and it must be accurately assessed for a correct extraction of predictive and prognostic biomarkers. Evaluation of preoperative (baseline) neoplasia/stroma ratio and the enumeration of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) represent only two conditions in which precise discrimination of cancer epithelium and stromal reaction are relevant.
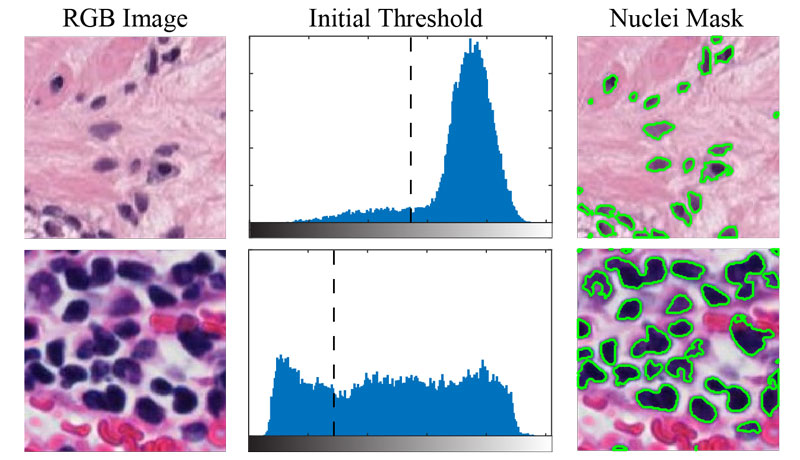
Multi-tissue and multi-scale approach for nuclei segmentation in H&E stained images
BioMedical Engineering OnLine | 20/06/2018Accurate nuclei detection and segmentation in histological images is essential for many clinical purposes. While manual annotations are time-consuming and operator-dependent, full automated segmentation remains a challenging task due to the high variability of cells intensity, size and morphology. Most of the proposed algorithms for the automated segmentation of nuclei were designed for specific organ or tissues.
